There are roughly 3,000 new cases of mesothelioma in the United States every year. Treatment for this disease may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy and immunotherapy.
Types of Mesothelioma
Malignant mesothelioma is often categorized based on where the primary tumor is located.
There are four main types of malignant mesothelioma.
-
- Pleural, found in the lining of the lungs (pleura)
- Peritoneal, originating in the tissue lining the abdominal wall (peritoneum)
- Pericardial, starting in the membrane surrounding the heart
- Testicular, starting in the tissue surrounding the testes
Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma

Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma, which accounts for about 75% of all diagnosed cases, affects the protective lining of the lungs, the pleura. However, it is not a type of lung cancer. If you’ve been diagnosed with pleural mesothelioma, you may have more treatment options available depending on the stage of the cancer.
Pleural Mesothelioma Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Difficulty breathing
- Persistent coughing
- Persistent chest pain
- Pleural effusion
- Weight loss
- Fever
Peritoneal Mesothelioma

Peritoneal mesothelioma affects the protective lining of the abdominal cavity, the area of your body containing several organs, including the stomach, intestines, kidneys and liver. The peritoneum abdomen lining is the second most common location where mesothelioma grows—about 20 to 24 percent of all mesotheliomas develop here.
Peritoneal Mesothelioma Symptoms
- Buildup of fluid in the abdominal cavity
- Weight loss
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Irregular bowel movements Abdominalpain
- Hernias
Pericardial Mesothelioma

Pericardial mesothelioma affects the protective lining of the heart called the pericardium, one of the rarest locations where mesothelioma occurs. Accounting for about 1 percent of all cases, pericardial mesothelioma is rare, which means that doctors don’t get to treat many patients with mesothelioma in this location and haven’t had many chances to create effective treatments.
Pericardial Mesothelioma Symptoms
- Chest pain
- Heart murmurs
- Excessive palpitations
- Labored breathing
- Fatigue
- Night sweats
Testicular Mesothelioma

Testicular mesothelioma is the rarest form of mesothelioma cancer and is found in the serous membrane, or “tunica vaginalis,” surrounding the testes in men. While it is considered highly aggressive and is known to metastasize rather quickly, testicular mesothelioma accounts for only 1% of diagnosed mesothelioma cases in the United States each year.
Testicular Mesothelioma Symptoms
- Appearance of a lump in the scrotum
- Swelling at the back of the testicles
- Scrotal discomfort
Diagnosing Mesothelioma Symptoms
The symptoms of mesothelioma make diagnosing the disease difficult. Symptoms take 10 to 50 years or more to appear after a person has been exposed to asbestos. The symptoms of mesothelioma are common in several other illnesses.
Doctors diagnose most patients when the disease has reached an advanced stage because the symptoms are nonspecific. If you or a loved one have a history of exposure to asbestos, and have felt any of the following symptoms, get in touch with one of our Mesothelioma Advocates. We can help get you the treatment you need to improve your prognosis and help you become a mesothelioma survivor.
Doctors may mistake breathing difficulty and persistent coughing — both symptoms of early–stage pleural mesothelioma — for pneumonia or another respiratory illness.
Causes of Mesothelioma
The only known cause of mesothelioma is exposure to asbestos, a naturally-occurring mineral used by many industries in materials ranging from wall insulation to brake pad lining.
How Asbestos Causes Mesothelioma
Asbestos is made of tiny fibers that break apart and become airborne very easily.

Malignant mesothelioma occurs when asbestos fibers get stuck in the mesothelium, a general name for the protective lining of a person’s lungs, abdomen, or heart.
If you’re exposed to damaged or disturbed asbestos-containing materials for a long period of time, you may inhale large amounts of microscopic asbestos fibers. Over time, they’ll collect in the mesothelium, where they cause irritation, inflammation, and cellular damage that leads to mesothelioma.
Most exposure to asbestos happens at work; 70 to 80 percent of patients diagnosed with mesothelioma had a history of asbestos exposure in the workplace.
Who Is At Risk?
Occupations where workers may experience this of exposure to asbestos include, but are not limited to:
Drywall Installers
Demolition Specialists
Mill Workers
Power and Chemical Plant Operators
Firefighters
Shipbuilders
Automobile Mechanics
Airplane Mechanics
70 to 80 percent of all patients report workplace exposure to asbestos.
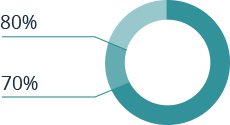
Veterans who served in the armed forces from the 1940s to the 1980s are most at-risk for developing malignant mesothelioma. Many military contractors used asbestos-containing products on ships, in barracks, in brake and clutch products, in gaskets and packing, and many other products and uses. In doing so, they exposed veterans to large amounts of asbestos, and increased their risk of developing mesothelioma. Veterans now account for 30 percent of all diagnoses in the U.S.
Discover How You Can Beat The Odds
Get your free mesothelioma guide and learn about your treatment options.
Get My Free GuideMesothelioma Diagnoses
Being diagnosed correctly is the first and most important step you’ll take towards getting treatment. If you’ve been exposed to asbestos in the past, and are feeling ongoing symptoms, see an experienced oncology doctor or other doctor. He or she may order an imaging test—like a chest x-ray, CT scan, or PET scan—to attempt to find visual signs of cancer or abnormalities. If the imaging scan shows anything that looks like a tumor or buildup of fluid, a doctor may order a blood test to make sure the next step in the diagnostic process, a biopsy, is necessary. If fluid is present, the fluid may be drained and tested to determine if you have mesothelioma or a biopsy may be performed.
A biopsy (or tissue sample) can help your oncologist determine the cell type of the disease—information he or she will use to create an effective treatment plan that can improve your prognosis.
Epithelial Cells
Epithelioid mesothelioma is the most common mesothelioma cell type, accounting for 70-80 percent of mesothelioma cases. When normal epithelial cells are exposed to asbestos fibers, they can mutate and, over time, become cancerous. Epithelioid mesothelioma is less aggressive than other types of mesothelioma. Epithelioid mesothelioma grows more slowly than other types of mesothelioma and tends to respond well to cancer treatment. As a result, mesothelioma patients with epithelioid mesothelioma may have a better prognosis. Life expectancy for patients with epithelioid mesothelioma is around 18-23 months, but can be much longer depending on the stage at the time of diagnosis and how effective treatment may be.
Sarcomatoid Cells
Sarcomatoid mesotheliomas are the most aggressive mesothelioma cell type. This type of mesothelioma is a rare cancer, accounting for 10-15 percent of pleural mesothelioma cases and 4 percent of peritoneal mesothelioma cases. Because these cancer cells have a characteristic spindle shape, this type of mesothelioma is often called spindle cell or sarcomatous mesothelioma. These cancer cells tend to be more difficult to diagnose and more resistant to treatment than other types of mesothelioma, which can lead to a worse prognosis. Patients with sarcomatoid mesothelioma may have a life expectancy that is shorter than 18 months. Recent clinical trial results have shown promising results for patients treated with immunotherapy.
Biphasic Cells
Biphasic, or mixed, mesothelioma contains both epithelioid and sarcomatoid cancer cells. To be considered biphasic mesothelioma, a patient’s tumor must have at least 10 percent of both sarcomatoid and epithelioid cells.
Because epithelioid cells are more responsive to treatment than sarcomatoid cells, the more epithelioid cells in a biphasic tumor, the better a patient’s prognosis. Similarly, the more sarcomatoid cells in a patient’s tumor, the worse a patient’s prognosis. Overall life expectancy for patients with biphasic mesothelioma may be less than 18 months. and delete the rest of the As with sarcomatoid mesothelioma, recent clinical trial results have shown promising results for biphasic or mixed mesothelioma patients treated with immunotherapy.
Stages of Mesothelioma
Your cancer stage is an important part of your malignant mesothelioma diagnosis. Along with its cell type, the stage of mesothelioma determines how effective treatment will be. Doctors haven’t created a staging system that’s specific to mesothelioma just yet, because the disease is rare. Instead, they use a number of systems—TNM, Butchart, and Brigham—specific to other cancers. Using different criteria, each system divides the spread of cancer into 4 stages. Generally speaking, the earlier the stage, the less mesothelioma has spread and the easier it is for surgeons to remove.
Stage 1

-
At stage one, the tumor only affects the area in the mesothelium where it originated (hasn’t yet spread to other organs). An early diagnosis can widen a patient’s eligibility for different treatment options.
- If you’re diagnosed with stage–one mesothelioma, you should respond well to treatment, and will enjoy a better prognosis than patients with advanced–stage mesothelioma.
Stage 2

- At stage two, the tumor has grown larger and may have spread to organs outside the area of where it first appeared in the mesothelium.
- Depending on your overall health, curative surgery is still an option for you–there’s not a substantial difference in prognosis between stage–one and stage–two patients.
Stage 3

- At stage three, the tumor has spread throughout one side of your body, and may have spread to other areas, including nearby lymph nodes, the esophagus, the chest wall, ribs, or heart.
- Tumors at this stage may not respond well to curative treatments, but surgery may still be an option. Your doctors will likely use palliative treatment to improve your quality of life.
Stage 4

- At stage four, the tumor has spread to both sides of the body. It may have invaded the brain, bone cells, far away lymph nodes, and other organ tissues.
- Most curative treatments, such as surgery and chemotherapy, are not effective in removing stage–four mesothelioma because it has spread so far. Doctors will instead use palliative treatment to relieve discomfort caused by symptoms. They may also enroll you in a clinical trial, where they’ll use new treatments to try and improve your prognosis.
Mesothelioma Treatment Options
If you’ve been diagnosed with mesothelioma, you have a number of treatment options, including surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Broadly speaking, your treatment will fall into 2 categories: curative or palliative.

Curative Treatment
With curative treatment, doctors extend your survival rate by removing as much of the mesothelioma as possible. They often combine multiple curative treatments to achieve amazing results.

Palliative Treatment
With palliative treatment, doctors treat the symptoms of mesothelioma rather than the cancer itself. The purpose of palliative care is to improve your quality of life by easing symptoms like chest or abdominal pain.
Doctors treat mesothelioma with a one-size-fits-all approach because the disease affects each patient differently. How your doctor uses surgery, chemotherapy or radiation therapy depends on your diagnosis—the cancer stage, cell type and location of the mesothelioma all play an important role in your treatment.
Surgery

The most effective is surgery if you’re diagnosed with stage 1 or 2 mesothelioma. This is because the disease hasn’t spread far beyond the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart. If you’re diagnosed with stage 3 or 4 mesothelioma, doctors use surgery to improve your quality of life by removing obstructive tumors.
Chemotherapy

Doctors use chemotherapy to shrink tumors, making their removal via surgery easier and more efficient. They also use it as a palliative measure to shrink tumors that restrict breathing, or cause excessive abdominal pain.
Radiation Therapy

Like chemotherapy, radiation therapy helps doctors remove tumors, and relieve discomfort caused by their obstructive growth.
Additional Treatment Options
Immunotherapy. Immunotherapy may be used as a replacement for chemotherapy. Immunotherapy uses the body’s own immune system to fight the spread or growth of the cancer cells. Immunotherapy, through a clinical trial, has been shown to have promising results for patients with sarcomatoid and biphasic mesothelioma. Learn More >
Multimodal Therapy. This is a combination of two or more treatments. Doctors have greatly increased the life expectancy of patients with pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma with multimodal therapy. Learn More >
New Treatments in Clinical Trials. Researchers are also developing new treatments, like immunotherapy and gene therapy, in clinical trials. Emerging treatments can benefit patients diagnosed with any stage of mesothelioma; if you’ve been diagnosed with advanced–stage mesothelioma, you may find an option to improve your prognosis. Learn More >
Your Prognosis
A prognosis is an estimate your doctor makes on how your diagnosis will affect you in the future; they base it on how diagnoses similar to yours affected other people in the past. The location, cell type, and cancer stage of the mesothelioma play a role your doctor’s estimate, and helps them decide which treatment options will work best for you.
Improving Your Prognosis
A prognosis is not set in stone—you can take action to change it by:
- Contacting a mesothelioma specialist
- Getting more exercise and eating healthy
- Reviewing all your treatment options
- Participating in clinical trials
You can also contact our Patient Help Team for more free information about mesothelioma, treatment, and how to improve your prognosis. A member of our team will have a conversation with you about your diagnosis, and can even help you find treatment to improve your prognosis.
Malignant Mesothelioma FAQs
Is mesothelioma always fatal?
There is no cure for mesothelioma, though some patients have been able to go into short-term remission. Mesothelioma caught in an early stage has a better prognosis with more treatment options available compared to later stages, leading to a better chance of long-term survival. Additionally, maintaining good overall health can improve your prognosis.
How many types of mesothelioma are there?
There are four types of mesothelioma, defined by where the cancer is found in the body:
-
- Pleural mesothelioma originates in the lining of the lungs, the pleura. This type of mesothelioma accounts for 75 percent of all diagnosed cases.
- Peritoneal mesothelioma originates in the lining of the abdomen, the peritoneum, and has the best life expectancy.
- Pericardial mesothelioma originates in the protective lining of the heart, the pericardium. It’s rare, accounting for about 1 percent of all diagnoses.
- Testicular mesothelioma originates in the tunica vaginalis membrane that surrounds the testes. Testicular mesothelioma is rare and accounts for less than one percent of all mesothelioma diagnoses.
Can asbestos fibers be removed after individuals have been exposed?
There are not currently any methods to remove asbestos fibers from the lungs. However, the lungs can clear some kinds of asbestos on their own.
What is the average life expectancy of a mesothelioma patient?
For all stages of mesothelioma combined, life expectancy is around 12-21 months. Mesothelioma prognosis is generally better for cancer found in earlier stages. Treatment can help improve life expectancy.
How quickly does mesothelioma spread?
Disease can take decades to appear following asbestos exposure. Late-stage (3-4) disease tends to progress more quickly than early-stage disease. Certain types of cancer cells, like sarcomatoid and biphasic mesotheliomas, are very aggressive and metastasize to other areas of the body quickly. Other cell types like epithelioid mesothelioma, are less aggressive.
- Sources
-
American Cancer Society. Malignant Mesothelioma. Accessed on 1/11/16. Retrieved from: http://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/cid/documents/webcontent/003119-pdf.pdf
-
National Institute of Health. Malignant Mesothelioma Treatment. Accessed on 1/11/16. Retrieved from: http://www.cancer.gov/types/mesothelioma/patient/mesothelioma-treatment-pdq
-
Environmental Protection Agency. Asbestos. Accessed on 1/11/16. Retrieved from: http://www.epa.gov/asbestos
-












